If you’ve recently upgraded to Windows 11 and noticed the absence of the Memory Integrity option, you’re not alone. Many users are confused when they find this setting missing, especially when others online are discussing its impact on performance. Let’s dive into what Memory Integrity is, why it may not be available for your system, and what you can do about it.
Understanding Memory Integrity
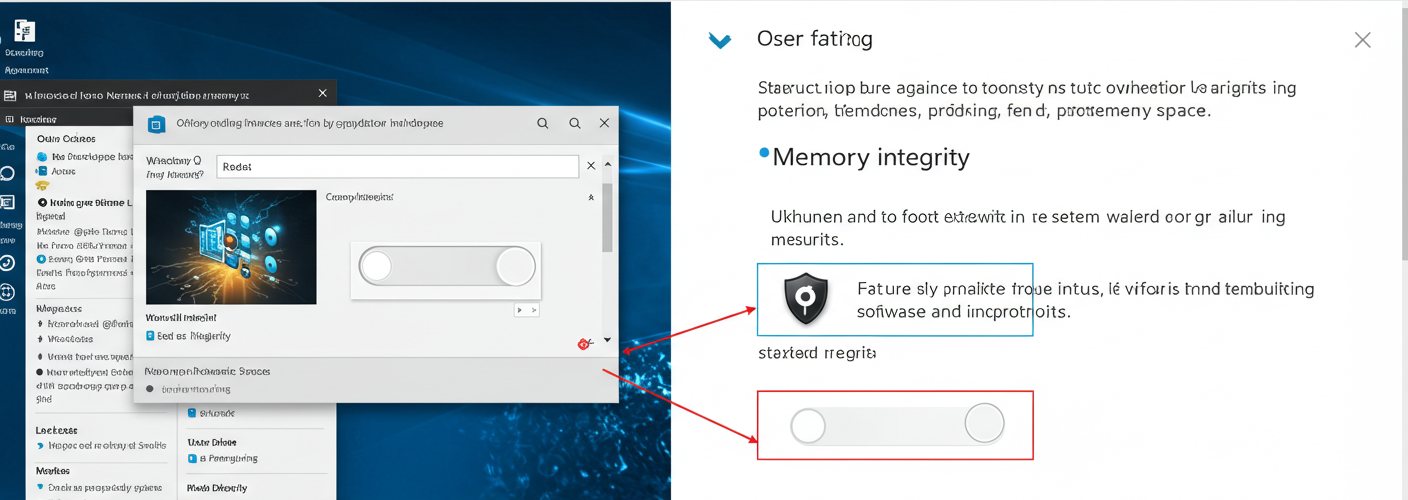
Memory Integrity, also known as Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI), is a security feature included in Windows 11 that uses virtualization-based security to help protect the system from malicious code. By isolating critical parts of the operating system, it aims to prevent unauthorized access and exploitation. However, users have reported that turning it off can lead to marginally improved frame rates (FPS) in games and performance-sensitive applications. This has led many to seek out this toggle in their security settings.
Reasons for Absence of Memory Integrity Option
- System Requirements: One of the primary reasons the Memory Integrity setting might not be available is if your hardware does not support it. Memory Integrity requires specific CPU features, such as virtualization support (Intel VT-x or AMD-V) and Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). If your device lacks these capabilities, the option won’t be displayed.
- Laptop vs. Desktop: Some system configurations, particularly those found in laptops, may have disabled features like Memory Integrity due to manufacturer specifications or power-saving settings. This is often seen in devices designed for a broader consumer base where performance in resource-intensive applications isn’t the primary focus.
- Windows Version: Ensure you are running the Pro or Enterprise version of Windows 11. Some security features, including Memory Integrity, may not be accessible in the Home version of the operating system. It’s essential to check the edition you have installed.
- Security Settings: Sometimes, security settings or group policies can interfere with your ability to access Memory Integrity. If your device is managed by an organizational policy, it may be locked down to prevent changes. It’s wise to check with your system administrator if this is the case.
- Outdated Drivers: Memory Integrity may also be unavailable due to outdated system drivers. To ensure that the option is visible, always keep your device’s BIOS and drivers up to date, particularly those related to virtualization technology.
What Should You Do?
If you’re looking to access the Memory Integrity feature but cannot find it, here are a few steps to troubleshoot:
- Verify Hardware Compatibility: Check your CPU specifications against Microsoft’s list of supported processors to see if Memory Integrity is feasible for your setup.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all relevant drivers, especially for virtualization support, are up-to-date. Tools like Windows Device Manager can help identify outdated drivers.
- Access Settings: Go to Windows Security > Device Security > Core Isolation Details. If the Memory Integrity toggle is missing, it may be due to one of the reasons outlined above.
- Contact Support or Community: If you’re still puzzled, consider reaching out to Microsoft support or visiting community forums, where you can share your specific device model and ask for insights from other users who may have faced similar issues.
In conclusion, while the absence of the Memory Integrity option may be disappointing, understanding the underlying reasons can help you determine whether performance tweaks or hardware adjustments are necessary. Always prioritize your system’s security when making decisions about features like Memory Integrity.




Add comment